Perceptron Algorithm, and Newton’s Method
본 글은 2018-2학기 Stanford Univ.의 Andrew Ng 교수님의 Machine Learning(CS229) 수업의 내용을 정리한 것입니다. 지적은 언제나 환영입니다 :)
Perceptron Algorithm
이번에는 Learning Algorithm의 역사적 배경 중 하나인 Perceptron Algorithm에 대해 살펴보자!
Perceptron Algorithm은 Logistic Regression의 sigmoid function $g(z)$를 약간 변형한 Threshold function을 사용한다.
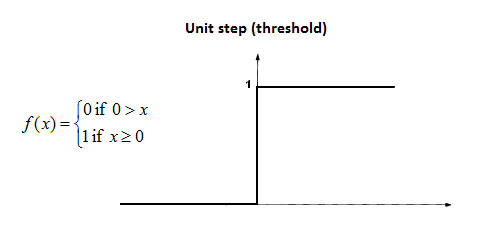
hypothesis $h_{\theta}(x)$를 $h_{\theta}(x)=g(\theta^{T}x)$로 두고 Learning rule을 기술해보면
앞선 Logistic Regression이나 Perceptron이나 동일한 rule로 $\theta$를 업데이트하는 모습을 볼 수 있다. 그러나, 둘은 $h_{\theta}(x)$가 다르기 때문에 엄연히 다른 알고리즘이다!
Perceptron은 1960년 대에 인간의 Neuron을 본뜬 모델이다. 하지만, Logistic Regression과 Linear Regression과는 달리 마땅한 통계학적 의미나 Maximum Likelihood Estimation과 접점이 없다.
Newton’s Method
$\theta$를 최적화하는 또다른 Iterative Learning을 살펴보자!
Newton’s Method는 real-valued function $f$에 대해 $f(\theta)=0$이 되는 $\theta$를 찾는 방식이다.
우리는 log likelihood $l(\theta)$를 Maximize하는 $\theta$를 찾는 것이 목표이다. 즉, $l’(\theta)$를 찾아야 하며, 이것을 Newton’s Method를 통해 찾을 수 있다!!
그리고 그 규칙은 다음과 같다.

Newton’s Method는 오직 linear function만을 사용해 함숫값이 0이 되는 지점을 찾는 가장 원초적인 방식이다.
Newton’s Method는 앞선 Gradient Descent 방식과 비교했을 때, 매우 적은 step으로 최적의 $\theta$를 얻는다.
우리가 원하는 $\theta$는 1D real-value가 아니라 N-dimensional real-valued vector이다. 그래서 Newton’s Method를 일반화해보자!
이것을 일반화하면
이다.
그리고 이것을 vector form으로 일반화하면 다음과 같다.
이때, $H$는 Hessian이다. vector function의 Derivate를 의미한다.
분명 Newton’s Method는 적은 step으로 최적의 $\theta$를 찾아낸다. 하지만, Newton’s Method의 공식을 살펴보면 n-by-n 행렬의 역행렬인 $H^{-1}$를 구하는 과정이 있다! n이 작다면 역행렬을 구하는 비용이 크지 않겠지만, n이 커진다면 역행렬을 구하는 비용은 아주아주 커진다… 그래서 Newton’s Method는 $\theta$가 갖는 feacture가 적을 때만 사용할 수 있다는 제약을 가진다.
맺음말
- Perceptron Algorithm은 가장 초기의 머신러닝 기법이다.
- 하지만, 통계학적 의미나 MLE와의 접점이 없다.
- Newton’s Method는 함숫값을 0으로 근사하는 가장 원초적인 접근법이다.
- Newton’s Method는 더 적은 step으로 최적해에 도달한다.
- 하지만, n-by-n 행렬인 Hessian $H$의 역행렬을 구하는 비용이 크다면 사용할 수 없다.
