Faster R-CNN
이 포스트는 제가 개인적인 용도로 정리하는 용도의 글 입니다.
ㄴ 내가 본 포스트 중에서 가장 잘 설명한 포스트다!
먄약 설명을 일일이 보는게 아니라 바로 전체 코드를 보고 싶다면 아래의 링크를 참조하자.
ㄴ link
- Region Proposal Network (RPN)
- RPN Loss Function
- ROI Pooling
- ROI Loss Function
RPN Network은 “Location”과 “Objectness”를 판단한다!
그렇게 RPN Network에서 생성한 proposal 중에서 가장 높은 $N$를 취한다!
이 top-$N$ proposal들을 Fast R-CNN network로 보낸다.
Fast R-CNN Network는 “location”과 “classification”을 수행한다.
VGG16을 feature extractor로 사용한다.
VGG16은 RPN network와 Fast R-CNN network 모두에서 backbone 네트워크로 사용된다!
Anchor Boxes
우리는 feature extractor인 VGG16을 통해서 800 x 800의 입력이미지를 50 x 50의 feature map으로 줄였다.
이때 50 x 50의 feature map의 각 픽셀은 16 x 16 pixels에 대응된다!
우리는 50 x 50의 feature map의 각 픽셀을 중심으로 삼는 anchor box들을 생성하게 된다.
이때, 크기와 종횡비가 각각 3개 있으므로 각 픽셀에 9개 모양의 anchor box가 생성된다.
그리고 anchor box는 [y1, x1, y2, x2]의 값을 가지므로
따라서 feature map의 각 픽셀에 (9, 4)의 anchor에 대한 Tensor가 할당되는 셈이다!
Q. Faster R-CNN에서 feature extractor가 꼭 50 x 50 사이즈의 faature map을 만들도록 디자인해야 하는 걸까?
“Note that single ground-truth object may assign positive labels to multiple anchors.” -> 당연!
“c) We assign a negative label to a non-positive anchor if its IoU ratio is lower than 0.3 for all ground-truth boxes. d) Anchors that are neither positive nor negative do not contribute to the training objective.”
argmax_ious: 각 anchor box가 어떤 gt-box와 더 큰 IoU를 갖는지에 대한 배열max_ious: 전체 IoU에서argmax_ious를 바탕으로 추출한max값!
max_ious 값을 바탕으로 각 anchor box에 positive / negative / none을 부여할 수 있음!!
조금 다른 방식으로는 threshold를 바탕으로 하는게 아니라 오직 max IoU에 대해서만 positive (1)을 부여한다면,
gt_argmax_ious: label에 관계 없이 가장 큰 IoU를 갖는 anchor box의 idx가 저장된 배열!
의 gt_argmax_ious를 이용할 수도 있음!
(단, 이 경우 negative를 매기는게 좀 tricky 하겠군…)
RPN 학습
전체 anchor를 생각해보면, positive anchor 보다 negative anchor의 수가 훨씬 많을 것이다. 또는 그 반대도 생길 수 있고. 많아 positivei-negative anchor 사이 불균형이 있다면, RPN을 학습시키지 좋지 않을 것이라고 Faster R-CNN 논문은 생각했다.
그래서 샘플링하는 수에 제한을 둬서 (ex: 256) 이 불균형 문제를 해소하고자 하였다.
Now we need to randomly sample #(positive samples) from the positive labels and ignore (-1) the remaining ones. In some cases we get less than #(positive samples), in that we will randomly sample (#(sample) — #(positive)) negative samples (0) and assign ignore label to the remaining anchor boxes. This is done using the following code.
BBox regression
(지엽) np.iinfo(), np.finfo()는 각각 int와 float에 대한 정보를 제공하는 함수다!
예를 들어, np.finfo(np.float32).min, np.finfo(np.float32).max, np.finfo(np.float32).eps 등으로
‘최솟값’, ‘최댓값’, ‘표현 가능한 가장 작은 값(machine epsilon)‘에 대한 정보를 알 수 있다!
// 근데 포스트에서 나오는 방식은 좀 과민 반응 같기도?
RPN Network Architecture
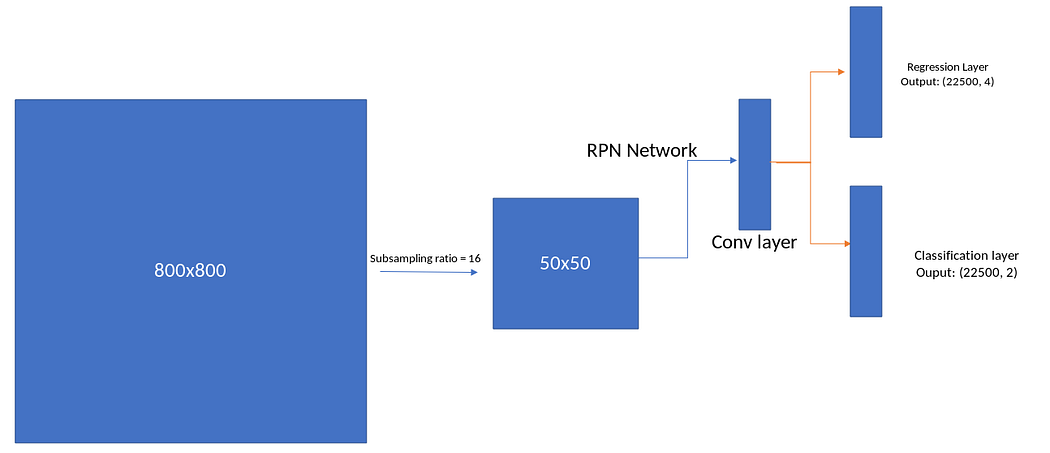
- RPN network(?) -> predict the location of the box “inside the anchor”.
To generate region proposals, we “slide” a small network over the convolutional feature map output.
This feature is fed into two sibling fully connected layers.
- A box regression layer
- A box classification layer
pred_cls_scores and objectness_scores are used as inputs to the proposal layer, which generate a set of proposal which are further used by “RoI network”.
아하! pred_cls_scores랑 objectness_scores가 되게 비슷하게 느껴졌는데 그 이유를 알았다!!
이게 objectness_scores는 background-ness와 object-ness에 대한 prediction 값을 가진 pred_cls_scores에서 object에 대한 score 부분만 추출한 거구나!
Generating proposals to feed Fast R-CNN network
“The Faster R_CNN says, RPN proposals highly overlap with each other. To reduced redundancy, we adopt non-maximum suppression(NMS) on the proposal regions based on their cls scores. We fix the IoU threshold for NMS at 0.7, which leaves us about 2000 proposal regions per image. After an ablation study, the authors show that NMS does not harm the ultimate detection accuracy, but substantially reduces the number of proposals. After NMS, we use the top-N ranked proposal regions for detection. In the following we training Fast R-CNN using 2000 RPN proposals. During testing they evaluate only 300 proposals, they have tested this with various numbers and obtained this.”
오홍! 학습 때와 테스트 할 때의 RPN proposal의 수가 다르구나!!
- convert the loc predictions from the rpn network to bbox [y1, x1, y2, x2] format.
- clip the predicted boxes to the image // 음?! 이건 좀 나중에 해도 될 것 같은데…?
- Remove predicted boxes with either height or width < threshold (min_size).
- Sort all (proposal, score) pairs by score from highest to lowest.
- Take top pre_nms_topN (e.g. 12000 while training and 300 while testing).
- Apply nms threshold > 0.7
- Take top pos_nms_topN (e.g. 2000 while training and 300 while testing)
아래의 수식을 통해 드디어 RPN을 완벽히 이해했다는 느낌이 들었다!!
- x = (w_{a} * ctr_x_{p}) + ctr_x_{a}
- y = (h_{a} * ctr_x_{p}) + ctr_x_{a}
- h = np.exp(h_{p}) * h_{a}
- w = np.exp(w_{p}) * w_{a}
and later convert to y1, x1, y2, x2 format
즉, “Proposal“이라는 것은 anchor box 내부에서의 정보를 담고 있는 것이다!
그래서 Proposal은 anchor와 함께 움직이는 존재라는 거지!
여기서 predicted_loc이 곧 Proposal이 되는 거지!
loc_layer는 Anchor 박스 내부에 존재할 Proposal을 만든다.
// 아님 anchor + predicted_loc을 Proposal로 이해해야 하나?
NMS
- while order_array.size > 0:
- take “the first element” in order_array and append that to keep
- Find the area with all other boxes
- Find the index of all the boxes which have high overlap with “this box”
- Remove them from order array
- Iterate this till we get the order_size to zero (while loop)
- Output the keep variable which tells what indexes to consider.
결국 NMS는 proposal 사이 사에서 IoU를 구해 proposal을 경량화하는 것!!
ROI Pooling layer
Region of interest pooling (also known as RoI pooling) purpose is to perform max pooling on inputs of non-uniform sizes to obtain fixed-size feature maps (e.g. 7×7). This layer takes two inputs
…
- Dividing the region proposal into “equal-sized sections” (the number of which is the same as the dimension of the output)
- Finding the largest value in each section
- Copying these max values to the output buffer
Note that “the dimension of the RoI pooling output” doesn’t actually depend on the size of the input feature map nor on the size of the region proposals. It’s determined solely by the number of sections we divide the proposal into.
What’s the benefit of RoI pooling? One of them is processing speed. If there are multiple object proposals on the frame, we can still use the “same-size input feature map” for all of them.
From the previous sections we got gt_roi_locs, gt_roi_labels and sample_rois. We will use the sample_rois as the input to the RoI pooling layer.

