Skyline Problem
2020-1학기, 대학에서 ‘알고리즘’ 수업을 듣고 공부한 바를 정리한 글입니다. 지적은 언제나 환영입니다 :) 전체 포스트는 Algorithm 포스트에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
백준 1933번: 스카이라인 문제를 다루는 포스트입니다 🙌
Given n rectangular buildings in a 2-dimensional city, computes the skyline of these buildings, eliminating hidden lines. The main task is to view buildings from a side and remove all sections that are not visible.
All buildings share common bottom and every building is represented by triplet (left, ht, right)
- ‘left’: is x coordinated of left side (or wall).
- ‘right’: is x coordinate of right side
- ‘ht’: is height of building.
A skyline is a collection of rectangular strips. A rectangular strip is represented as a pair (left, ht) where left is x coordinate of left side of strip and ht is height of strip.
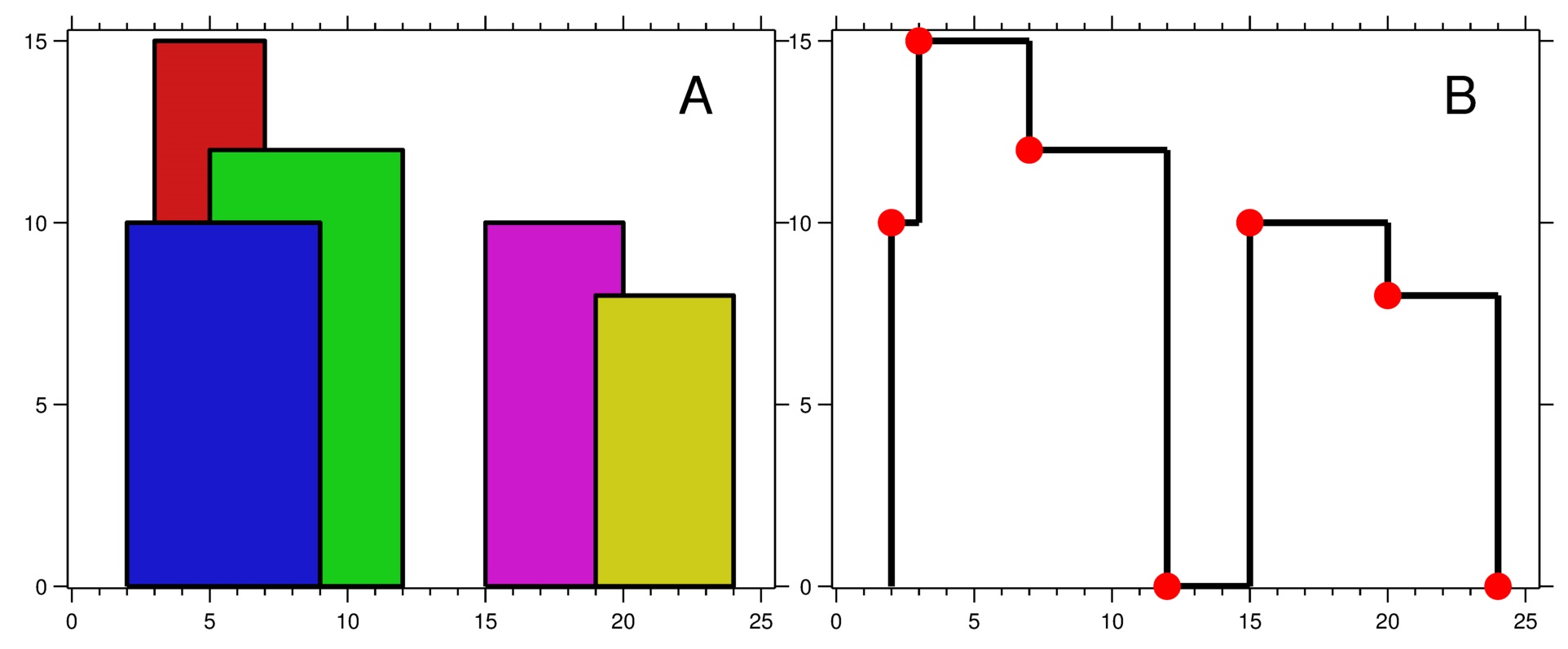
<Skyline Problem>은 여러 개의 직사각형 빌딩에서 그들의 테두리인 skyline을 계산하는 문제이다. 출력 형식을 보면 알 수 있듯이 높이(ht)가 변할 때의 x 지점만 (x, ht)로 출력해주면 된다. <Brute Force>와 <Divide and Conquery>로 문제를 해결해보자!
Brute Force
1. Mark key points for each given building.
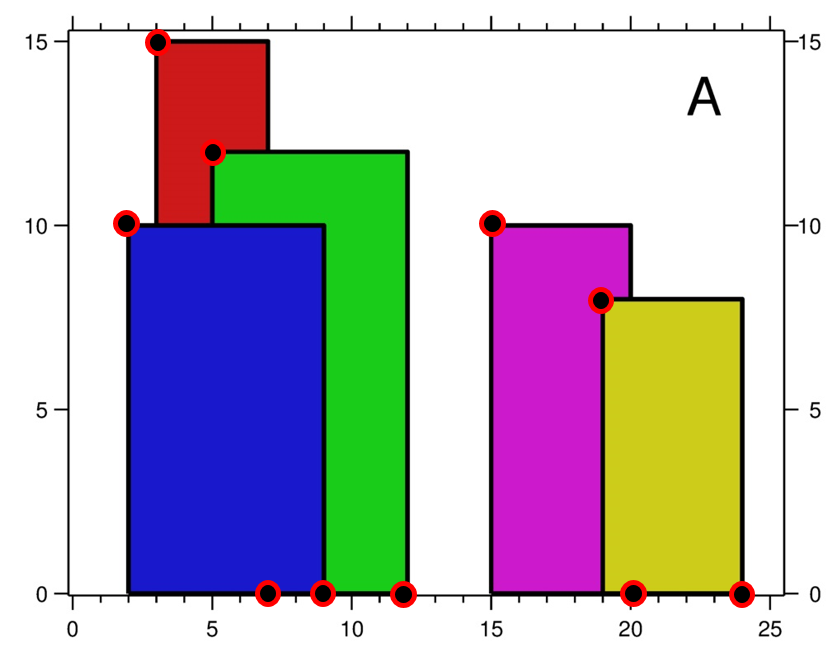
[left, ht, right] 형식의 각 빌딩을 [left, ht], [right, 0] 형식으로 바꿔준다.
2. For each marked key point, if there exist heighter key points overlap it, then change its y as the height of tallest overlapping building.
왼쪽에서 오른쪽 방향으로 천천히 따라가보자!
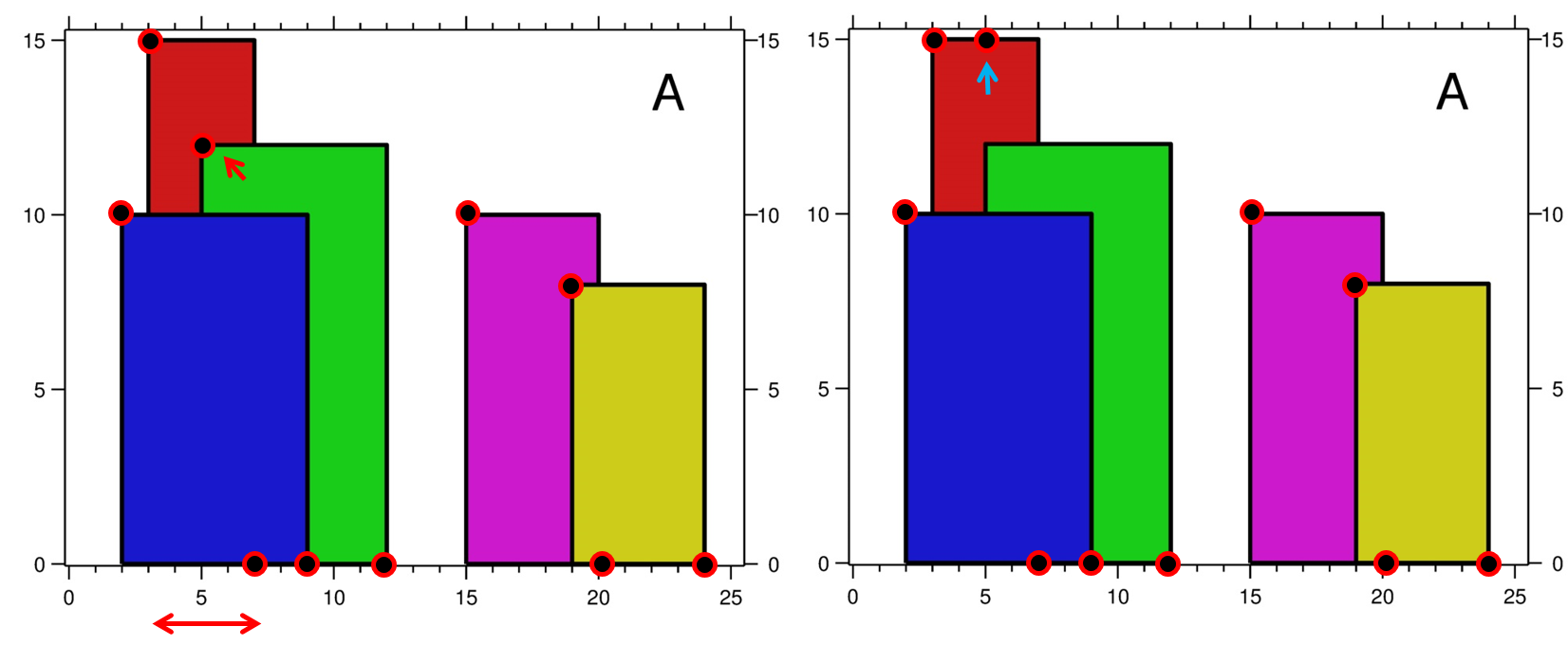
먼저 초록색 빌딩의 [left, ht] 점은 빨간색 빌딩에 overlapping 되기 때문에 y 값을 갱신한다. 이때, [left, ht] 값 자체를 갱신하는게 아니라 갱신된 [left, ht_new]를 result array vector<point> ret에 넣어두면 된다.
이 방법을 계속하면…
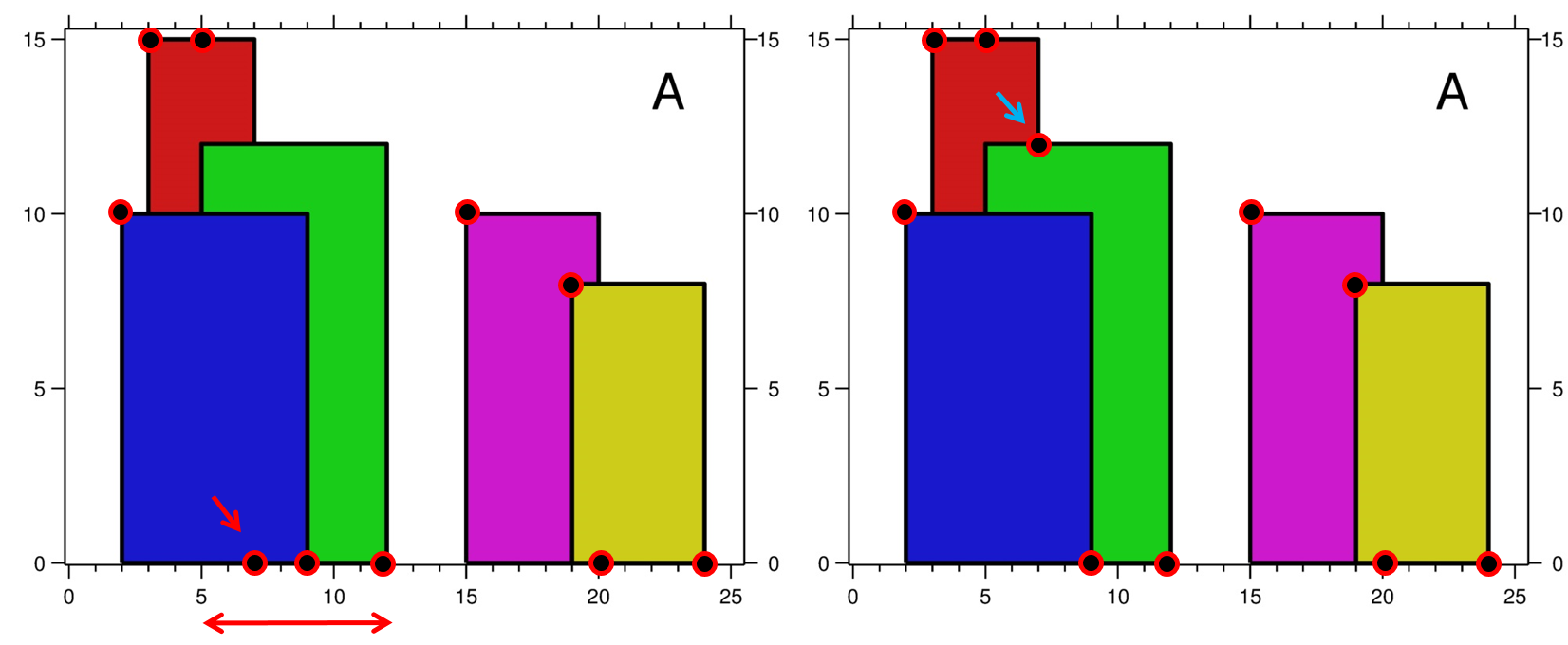
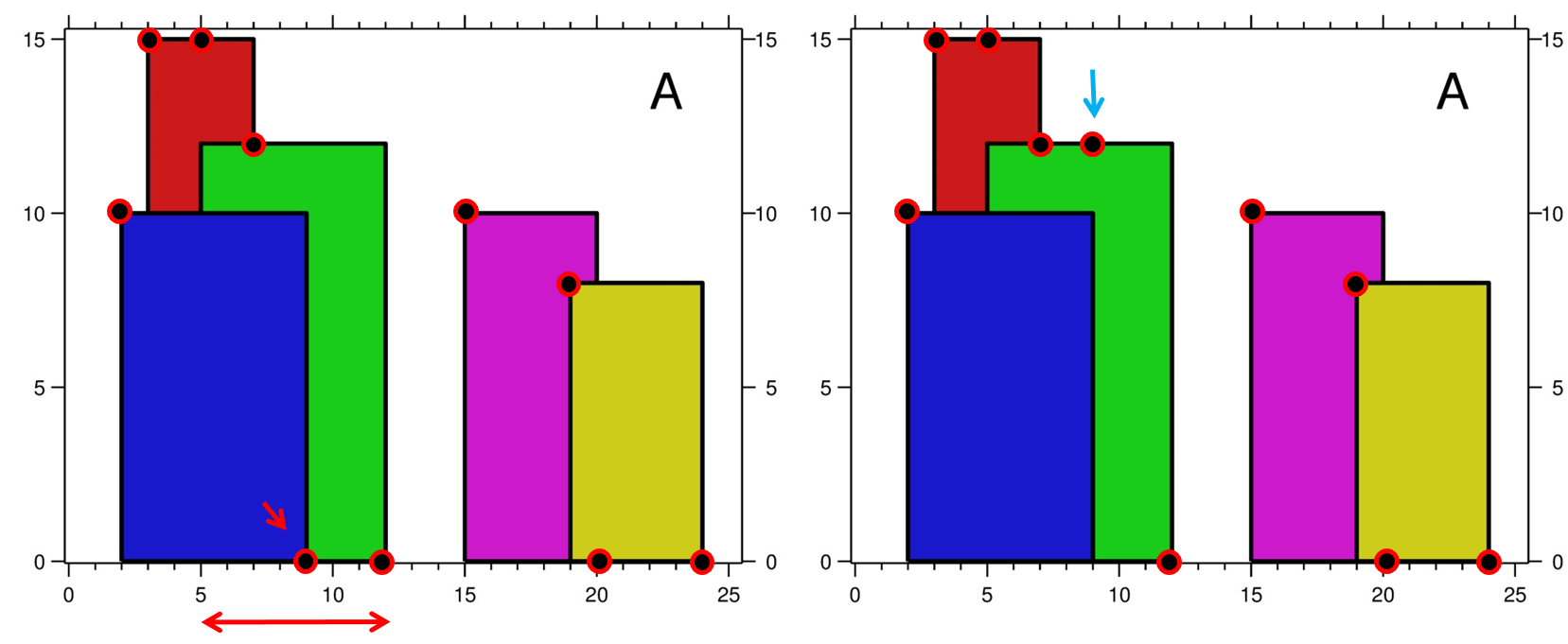
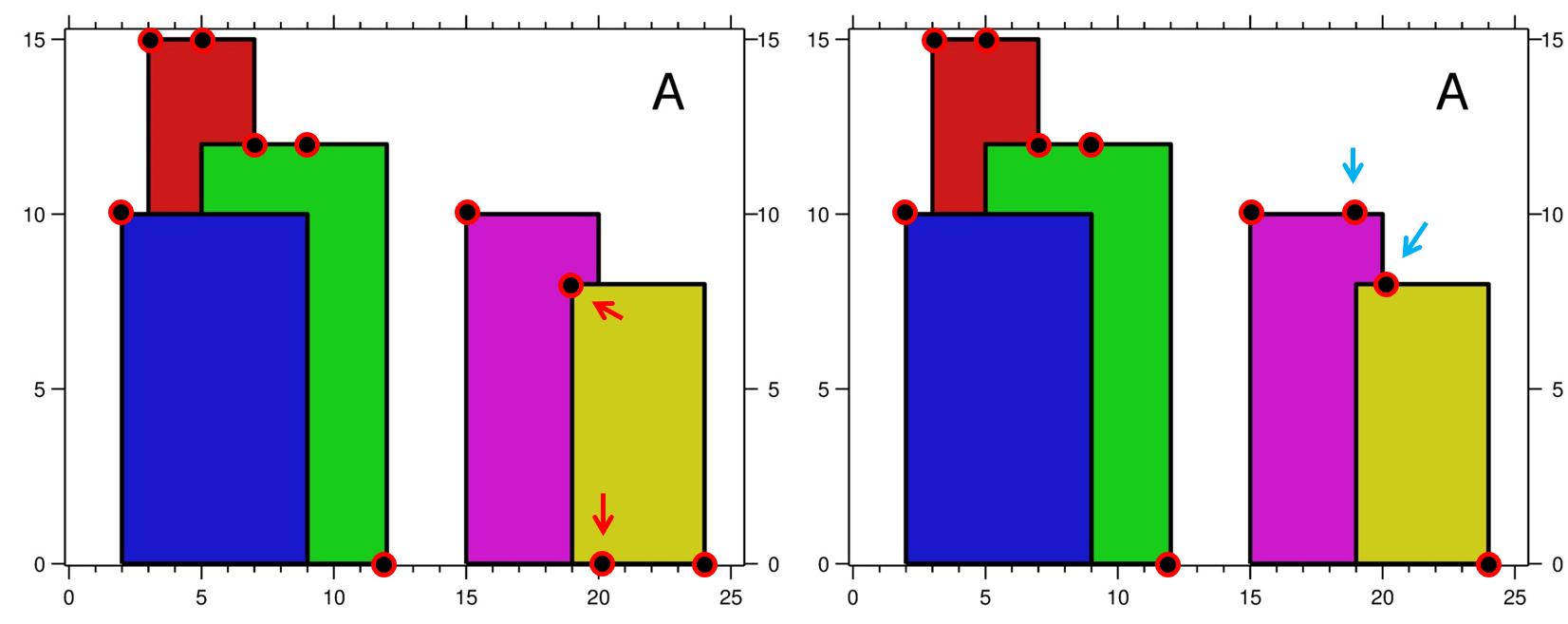
모든 key point를 다 돌았다면, vector<point> ret에서 y 값이 중복되는 점들을 제거하면 된다.
각 key point의 overlap 되는 tallest building을 찾기 위해 building 배열을 순회한다: $O(n)$. 따라서 $n$개 key point를 처리하는데 $O(n)$ 만큼의 연산이 필요하므로, Brute Force 방식은 $O(n^2)$의 시간복잡도를 갖는다.
Brute Force 풀이
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100005
typedef pair<int, int> Coord;
typedef pair<pair<int, int>, int> Building;
vector<Building> blding;
vector<Coord> key_points; // collection of key points
vector<Coord> ret;
int main() {
int N;
scanf("%d", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int l, h, r;
scanf("%d %d %d", &l, &h, &r);
blding.push_back({ { l, r }, h });
key_points.push_back({ l, h });
key_points.push_back({ r, 0 });
}
sort(key_points.begin(), key_points.end());
// process key points!
for (Coord &point : key_points) {
int x = point.first, y = point.second;
int max_h = y;
for (Building &building : blding) {
int b_left = building.first.first, b_right = building.first.second;
if (b_left > x || b_right <= x) continue;
max_h = max(max_h, building.second);
}
ret.push_back({x, max_h});
}
// show intermediate result
for (int i = 0; i < ret.size(); i++) {
printf("(%d %d) ", ret[i].first, ret[i].second);
}
printf("\n");
// process redundant key points
// how? compare with behind
vector<Coord> final_ret;
final_ret.push_back(ret[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < ret.size(); i++) {
int prev_h = ret[i - 1].second;
int curr_h = ret[i].second;
if (prev_h != curr_h) {
final_ret.push_back(ret[i]);
}
}
// show final result
for (int i = 0; i < final_ret.size(); i++) {
printf("%d %d ", final_ret[i].first, final_ret[i].second);
}
return 0;
}
당연히 시간초과가 나니 제출하지 말 것!
Divide and Conquer (feat. Merge Sort)
이번에는 다른 방법으로 이 문제를 풀어보자. 제목은 <Divide-and-Conquery>지만 핵심적인 아이디어는 <Merge Sort>다.
일단 <Merge Sort>의 방식대로 문제를 절반씩 나누어 해결한 후, 그 결과를 <Merge>할 예정이다. 먼저 절반씩 나누는 것부터 살펴보면,
vector<Coord> skyline(vector<Building> buildings) {
if (buildings.size() == 0) {
return vector<Coord>();
} else if (buildings.size() == 1) {
int l = buildings[0].first.first, r = buildings[0].first.second, h = buildings[0].second;
return vector<Coord>({ {l, h}, {r, 0} });
} else {
int mid = buildings.size() / 2;
vector<Coord> left_side = skyline(vector<Building>(buildings.begin(), buildings.begin() + mid));
vector<Coord> right_side = skyline(vector<Building>(buildings.begin() + mid, buildings.end()));
return merge(left_side, right_side);
}
}
입력받은 vector<Building>을 절반씩 나누어 결과를 도출한 후 merge()를 통해 합친다. 자, 그럼 어떻게 2개의 vector<Coord>를 적절히 합치느냐가 중요해졌다!! 👊
2개의 skyline 배열을 merge하는 방법은 아래와 같다.
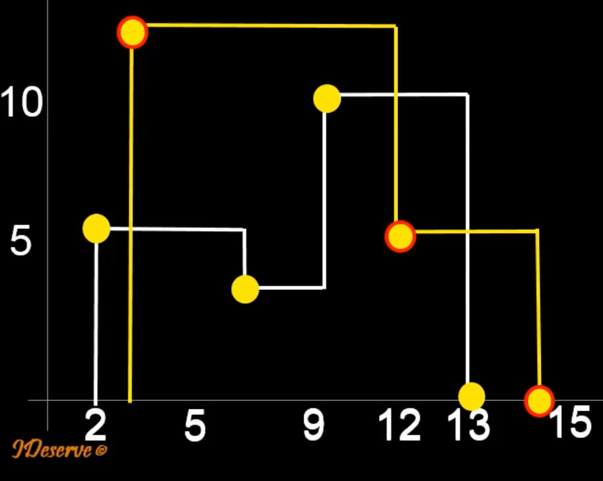
1. Let’s compare key points of skylines starting from the leftmost end.
2. For two key points of two skylines, choose the one skyline having key point with lesser x value.
3. If y value of chosen key point is less than the last seen height of other skyline. then update key point’s y to the last seen height of other skyilne.
4. Proceed to next key point of the chosen skyline.
5. Repeat [2-4] steps until both the skylines are completed.
6. Remove the redundant key points.
자! 그럼 위의 알고리즘을 단계별로 수행해보자.
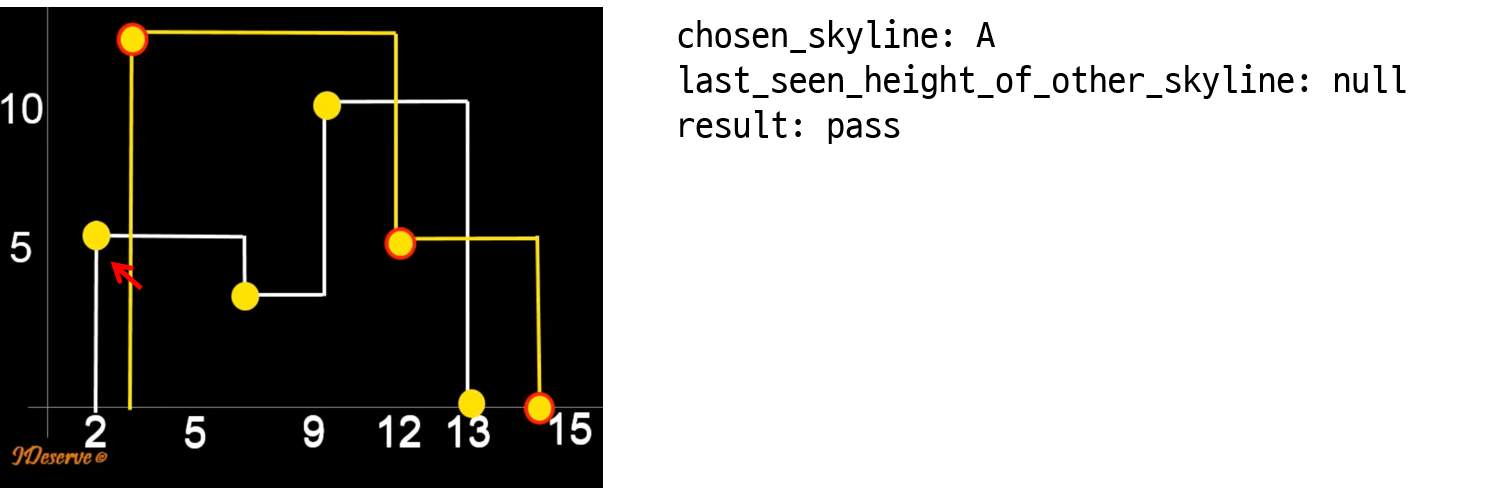
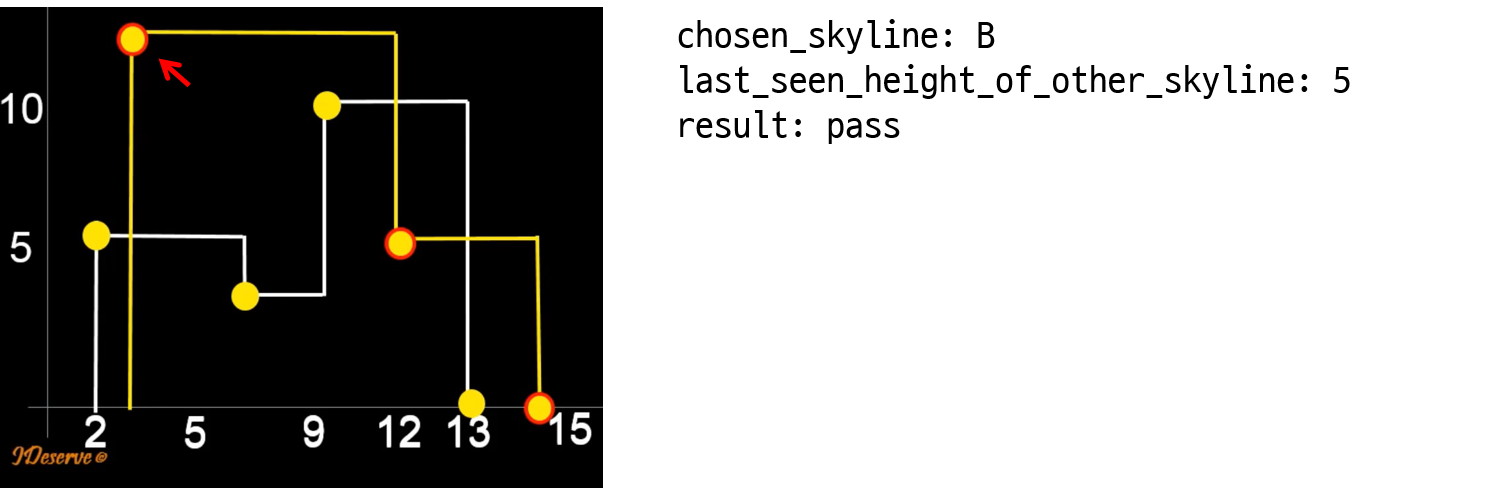
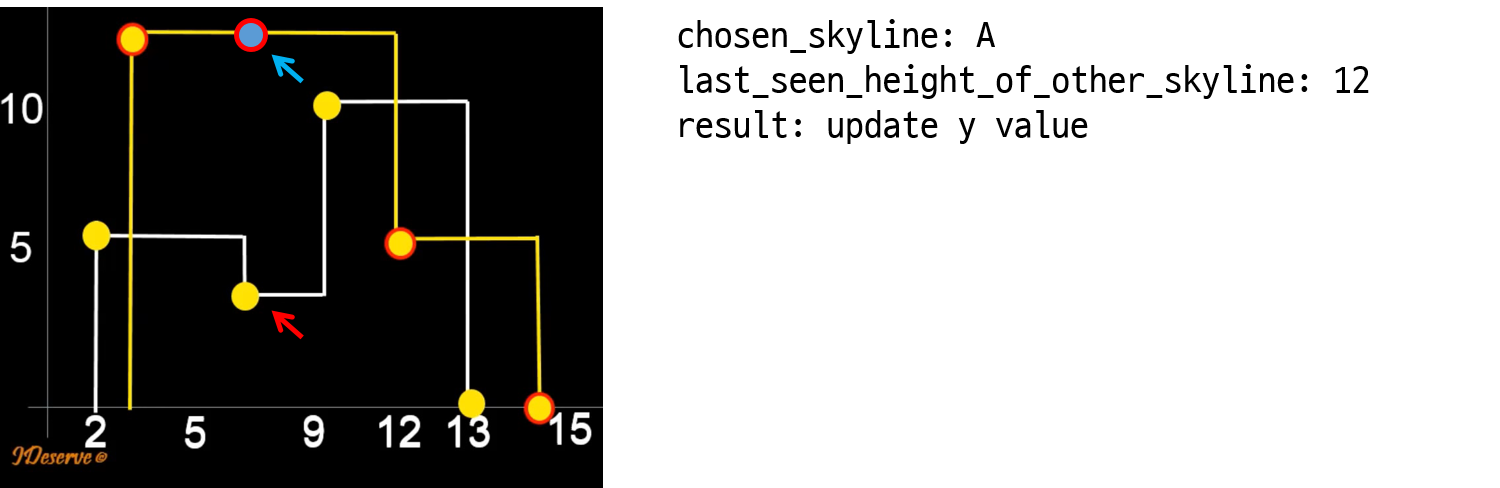
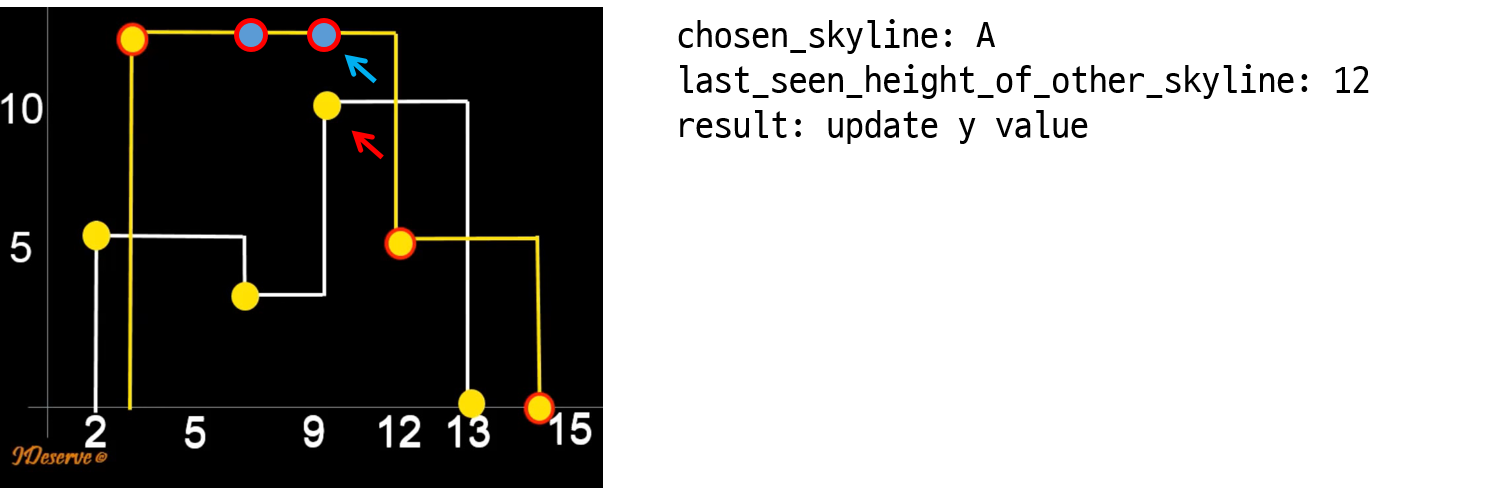
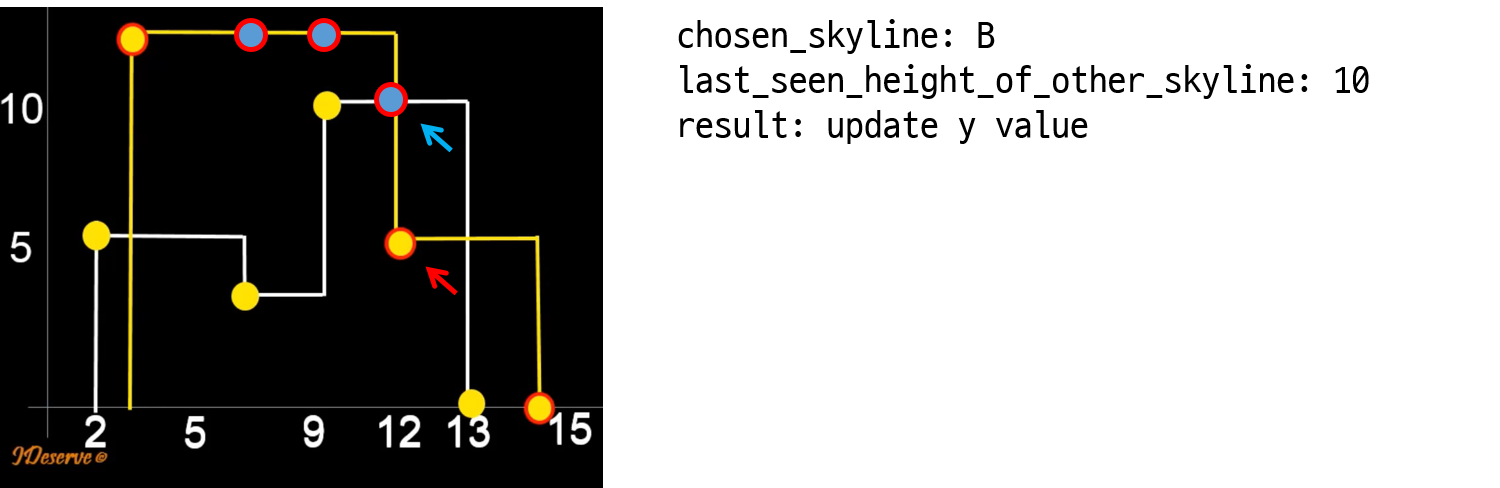
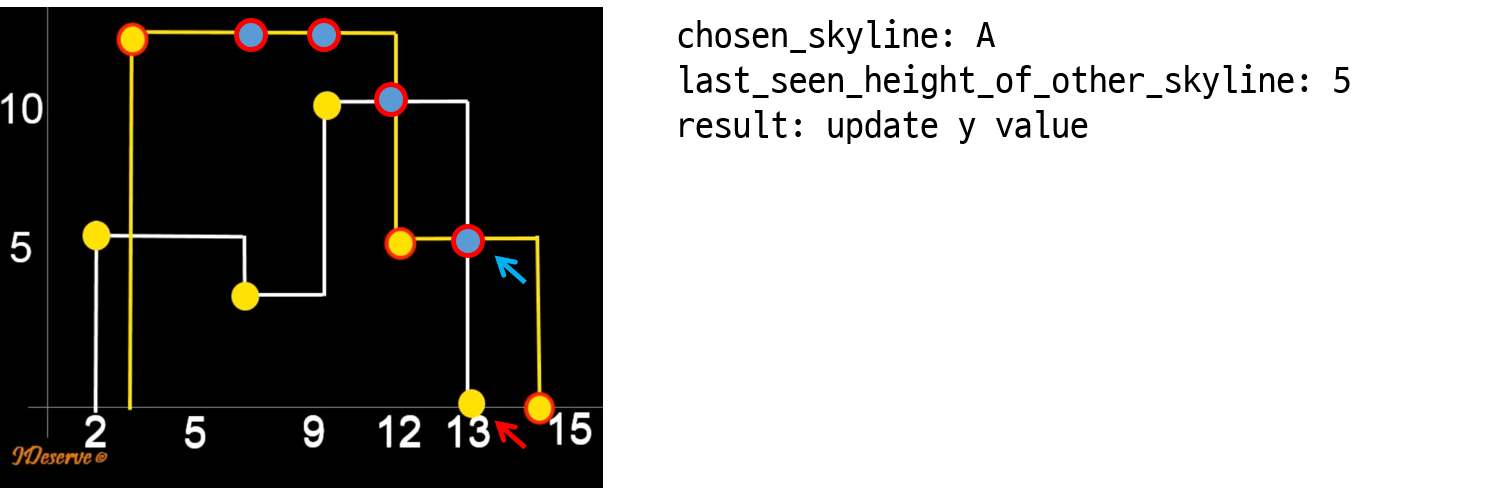
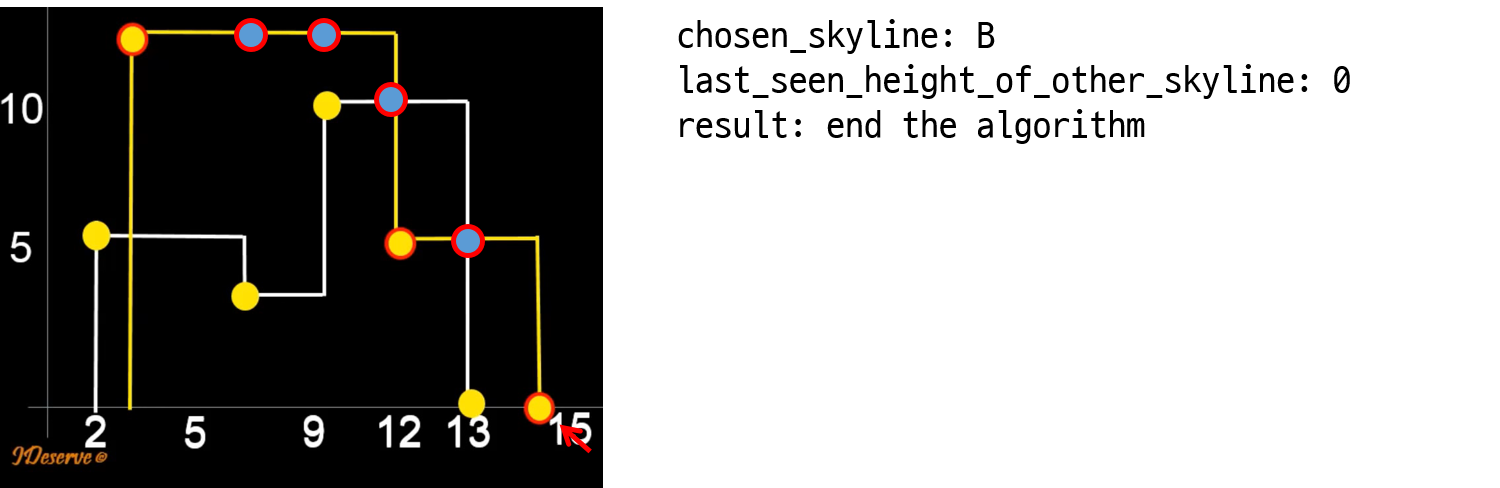
와우!! 놀라운 방법으로 두 skyline을 merge 했다!! 😲 코드로 작성하면 아래와 같다.
vector<Coord> merge(vector<Coord> left_side, vector<Coord> right_side) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
int last_h1 = -1, last_h2 = -1;
vector<Coord> ret;
while (i < left_side.size() && j < right_side.size()) {
Coord p1 = left_side[i], p2 = right_side[j];
if (p1.first < p2.first) {
ret.push_back({p1.first, max(p1.second, last_h2)});
last_h1 = p1.second;
i += 1;
} else if (p1.first > p2.first) {
ret.push_back({p2.first, max(p2.second, last_h1)});
last_h2 = p2.second;
j += 1;
} else {
// see later
}
}
for (; i < left_side.size(); i++) {
ret.push_back(left_side[i]);
}
for (; j < right_side.size(); j++) {
ret.push_back(right_side[j]);
}
// process redundants
vector<Coord> final_ret;
final_ret.push_back(ret[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < ret.size(); i++) {
int prev_h = ret[i - 1].second;
int curr_h = ret[i].second;
if (prev_h != curr_h) {
final_ret.push_back(ret[i]);
}
}
return final_ret;
}
그러나 위의 merge 알고리즘에서 우리는 두 key point의 x 값이 같은 경우를 다루지 않았다!
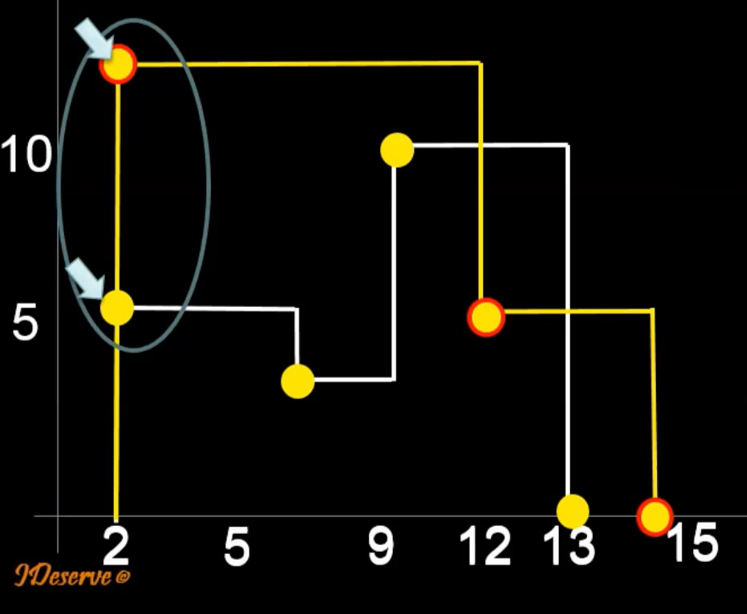
이 경우는 아래와 같이 해결한다.
If x values of both key points are same, then choose the one with higher y value and advance key points for both skylines.
그래서 위의 코드에서 해당 부분을 채우면 아래와 같다.
if (p1.first < p2.first) {
ret.push_back({p1.first, max(p1.second, last_h2)});
last_h1 = p1.second;
i += 1;
} else if (p1.first > p2.first) {
ret.push_back({p2.first, max(p2.second, last_h1)});
last_h2 = p2.second;
j += 1;
} else {
ret.push_back({p1.first, max(p1.second, p2.second)});
last_h1 = p1.second;
last_h2 = p2.second;
i += 1;
j += 1;
}
이것으로 <Skyline Problem>에 대해 살펴보았다. 한 가지 풀이법이 더 있다고 하는데, <우선순위 큐>를 이용하는 방식이다. 이 녀석은 나중에 시간이 나면 정리하도록 하겠다 😉
