Istio Circular Virtual Service
 오늘의 주제는 꼬리에 꼬리를 무는, 무한번 호출이다!
오늘의 주제는 꼬리에 꼬리를 무는, 무한번 호출이다!
Istio의 VirtualService의 동작을 이해하려고 할 때, 이해가 안 되는게 spec.hosts에도 host 주소를 적고, destination 속성에도 host 주소를 적는 거 였다.
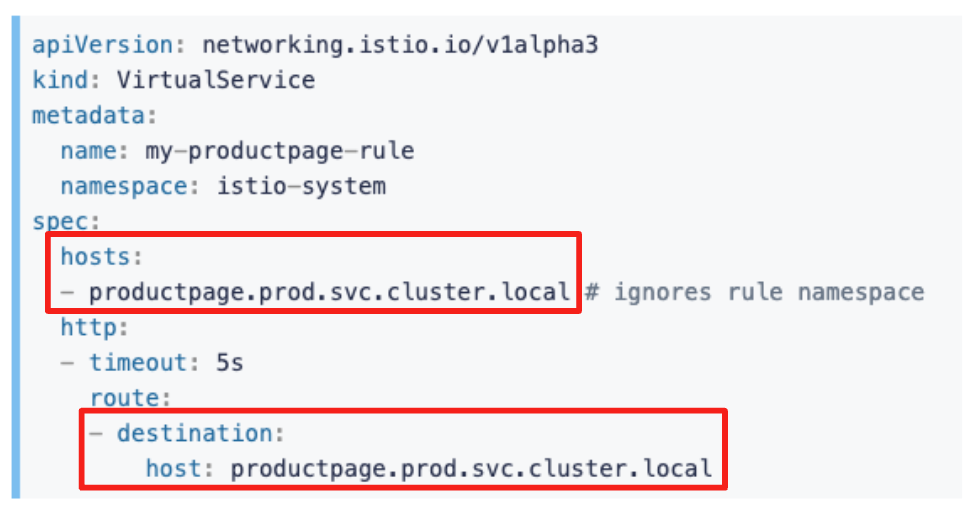
그런 나에게 이런 질문이 떠올랐는데…
- “만약 자기 자신을 destination으로 갖는 VirtualService를 띄우면, 이 VirtualService는 무한번 evaluation 되는 걸까?”
- “만약 VirtualService로 host A의 트래픽을 host B로 보내고, 또 다른 VirtualService로는 host B는 다시 host A로 트래픽을 보낸다면, 이 경우도 evaluation이 무한번 되는 걸까?”
뭔가 “무한번” evaluation 되는 것에 대한 궁금증이 생겼고, 직접 해당 케이스들을 클러스터에 띄워 실험해보았다!
다시 helloworld 예제를 띄우자
$ kubectl apply -n default -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/1.20.2/samples/helloworld/helloworld.yaml
service/helloworld created
deployment.apps/helloworld-v1 created
deployment.apps/helloworld-v2 created
그런데 svc/helloworld가 있으니 트래픽 분산이 뭔가 잘 안 되는 것 같아서 svc/helloworld는 지워두자!!
$ kubectl delete svc/helloworld
하고 v1, v2 버전에 API call을 보낼 수 있도록 각각의 K8s Service 리소스를 만들어두자.
$ kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: helloworld-v1
labels:
app: helloworld
service: helloworld
version: v1
spec:
ports:
- port: 5000
name: http
selector:
app: helloworld
version: v1
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: helloworld-v2
labels:
app: helloworld
service: helloworld
version: v2
spec:
ports:
- port: 5000
name: http
selector:
app: helloworld
version: v2
EOF
아, 그리고 helloworld v1, v2에 트래픽을 흘려보낼 테스트용 nginx Pod도 하나 띄우자.
$ k run nginx --image=nginx
$ k exec -it nginx -- sh
# <on some pod>
while true; do curl "http://helloworld.default:5000/hello"; done
좋았어!! 준비는 끝났다!! (´∀`)b
무한 Evaluation이 일어날지 실험
자기 자신으로 라우팅 하는 Virtual Service
“만약 자기 자신을 destination으로 하는 VirtualService를 띄우면, 이 VirtualService는 무한번 evaluation 되는 걸까?”
# self-destination.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: self-destination
spec:
hosts:
- "helloworld-v1.default.svc.cluster.local"
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: helloworld-v1.default.svc.cluster.local
요런 VirtualService를 만들고, nginx Pod에 접속해서 트래픽을 흘려보자.
$ k exec -it nginx -- sh
# <on some pod>
while true; do curl "http://helloworld-v1.default.svc.cluster.local:5000/hello"; done
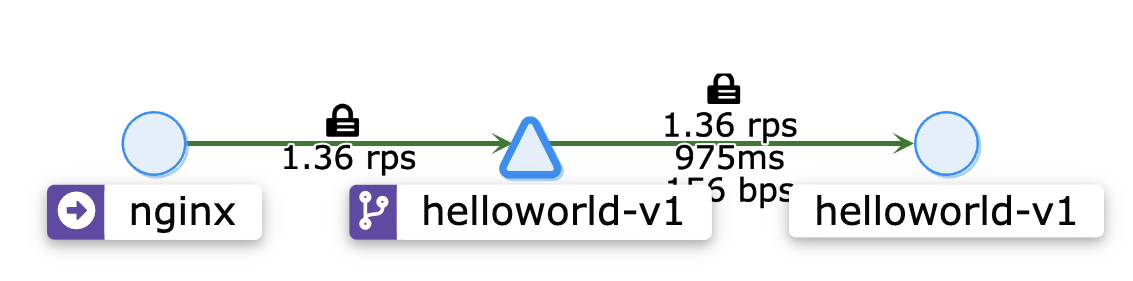
흐음…?
만약 무한번 Evaluation이 일어났다면, timeout이 발생했을 것 같은데, 자기 자신으로 트래픽이 잘 가고 있다!!
서로에게 트래픽을 보내 버리는 Virtual Service

서로 트래픽을 미루는 VirtualService를 구성해보자.
# circular-traffic-shift.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: traffic-shift-v1-to-v2
spec:
hosts:
- "helloworld-v1.default.svc.cluster.local"
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: helloworld-v2.default.svc.cluster.local
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: traffic-shift-v2-to-v1
spec:
hosts:
- "helloworld-v2.default.svc.cluster.local"
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: helloworld-v1.default.svc.cluster.local
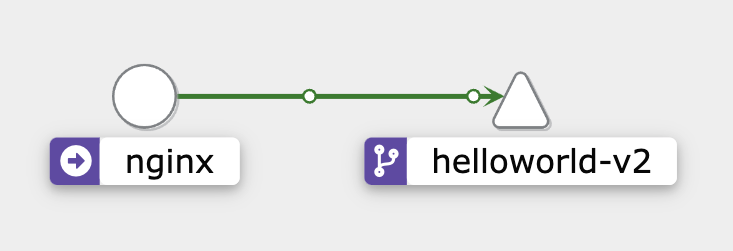
뭔가 예상하기로는 v1이랑 v2가 번갈아 가면서 나올 줄 알았는데, vs/traffic-shift-v1-to-v2에 명시한 대로 트래픽이 오직 v2로만 잘 가고 있다!!
결론
무한번 Evaluation이 일어나지 않는 이유는, Envoy Proxy가 동작하는 방식에 있다.
일단 Envoy Proxy는 앱에서 in/out 하는 트래픽을 대신 컨트롤 하는 녀석이다. 그래서 nginx가 helloworld-v2.default에 요청을 보낸다면, 현재 Service Mesh에 정의된 VirtualService 중에 저곳을 hosts로 갖는 VirtualService를 찾은 후, 그 ViritualService의 규칙을 적용한다.
이때, Envoy Proxy가 트래픽을 helloworld-v1.default로 보내라고 정했으면 추가적인 evaluation은 더이상 없다! 즉, 다시 helloworld-v1.default를 hosts로 갖는 VirtualService를 찾지는 않는다는 것이다.
나가는 트래픽에는 VirtualService 규칙을 적용
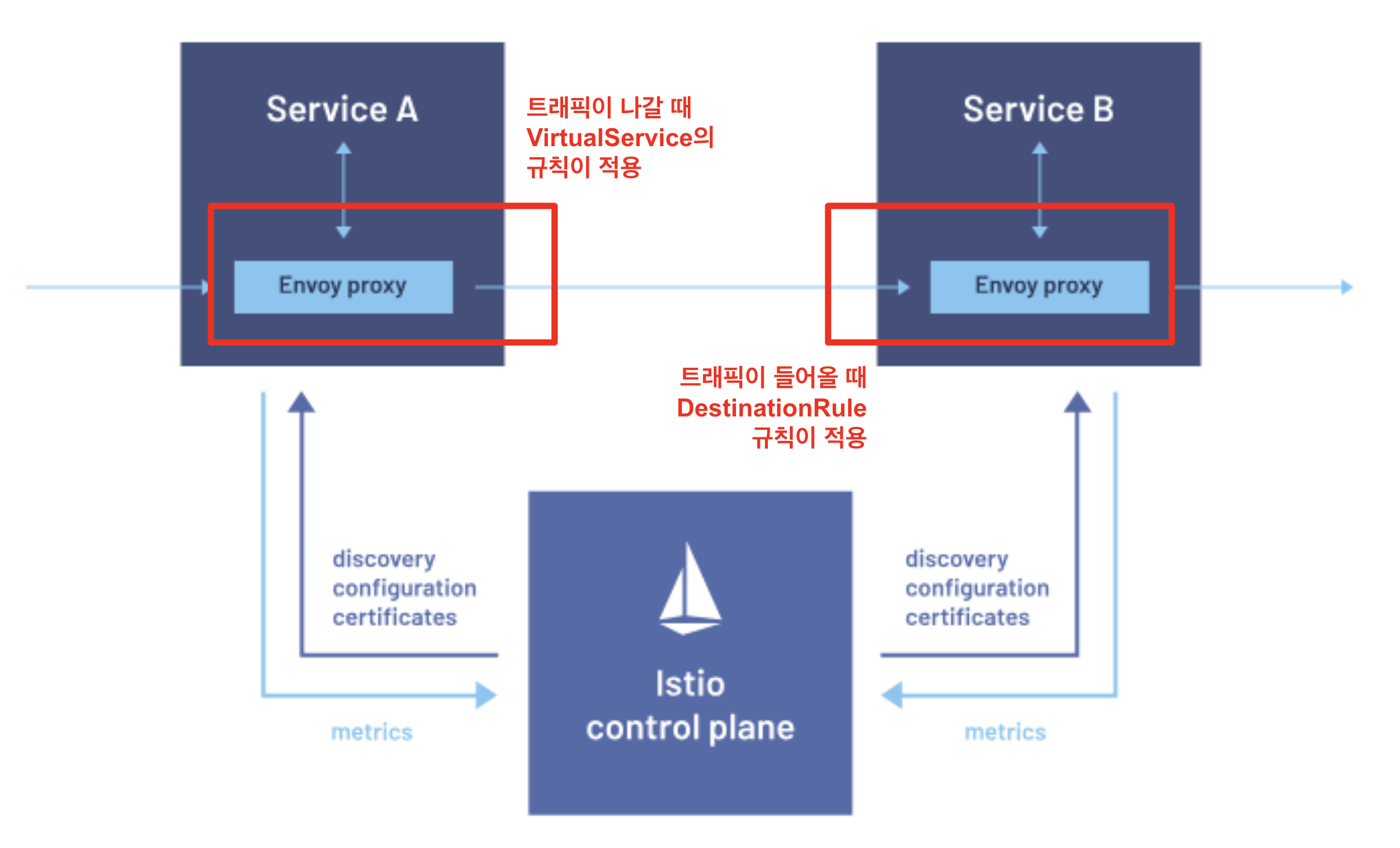
어떻게 보면 내가 착각한 부분은 VirtualService가 evaluation 되는 지점이 트래픽이 도달하는 Pod의 Envoy Proxy라고 생각했기 때문인 것 같다. 그러나 실제론 그 과정이 트래픽을 보내는 Pod의 Envoy Proxy에서 진행 되었다.
그렇기 때문에 VirtualService에는 Istio Service Mesh 외부의 host들도 hosts와 destination에 적을 수 있다.
naver.com으로 가는 트래픽을 외부가 아니라 내부의 다른 Pod으로 보내버린다거나 미러링 하도록 VirtualService로 설정할 수 있다.
또, VirtualService 규칙은 Envoy Proxy가 없는 Pod에서는 적용되지 않는 점도 VirtualService의 규칙이 트래픽을 보내는 Pod의 Envoy Proxy에서 일어나기 때문이다.
들어오는 트래픽에는 DestinationRule 규칙을 적용
반대로 트래픽이 도달하는 Pod의 Envoy Proxy에서는 DestinationRule의 evaluation이 일어난다!!
예를 들어,
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: helloworld-v1-max-connection
spec:
host: helloworld-v1.default.svc.cluster.local
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http:
http2MaxRequests: 1
요렇게 DestinationRule을 설정하면, 오직 한번에 하나의 http request만 허용하도록 적용해보자.
요렇게 하면, nginx Pod에 접속하는 터미널 2개를 열어서 아래 요청을 보내면 이런 현상을 볼 수 있다.
$ while true; do curl "http://helloworld-v2.default.svc.cluster.local:5000/hello"; done
(DR 설정은 helloworld-v1.default에 했는데, 앞에서 VS 설정 한게 있어서 helloworld-v2.default에 요청을 보낸다!!)
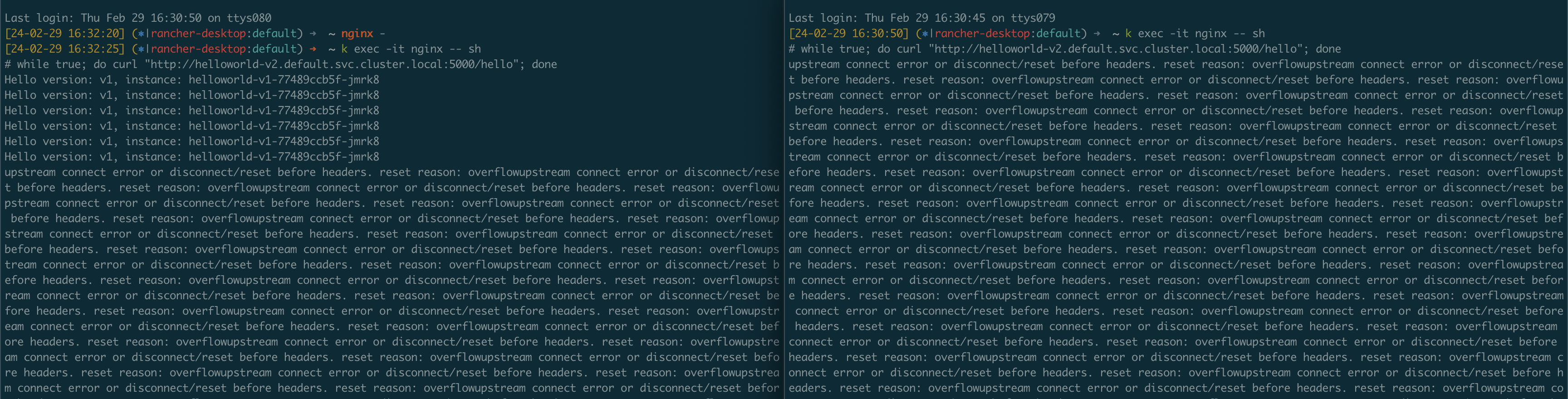 잘 안 보이니 확대 해서 보자
잘 안 보이니 확대 해서 보자
캡쳐를 보면 처음에는 v1으로 요청이 잘 가다가, 다른 터미널에서도 요청을 보내기 시작하면서 reset reason: overflowupstream connect error or disconnect/reset before headers 에러를 받게 된다.
신기한 점은 분명 요청은 helloworld-v2로 보냈는데, helloworld-v1의 DR 룰에 의해 upstream overflow가 발생 했다는 것이다.
또, 만약 Istio Service Mesh 바깥의 Pod이 DR이 설정된 helloworld-v1.default에 요청을 보내도, 똑같이 이 max http request의 규칙을 적용 받는 것이다!! 이 또한 DestinationRule이 트래픽을 받는 쪽의 Envoy Proxy에서 적용 되기 때문이다!
즉, 이 경우 트래픽을 받는 쪽의 DestinationRule이 적용된 거라고 볼 수 있다.
