Independent Set, Vertex Cover, and Clique
2020-1학기, 대학에서 ‘알고리즘’ 수업을 듣고 공부한 바를 정리한 글입니다. 지적은 언제나 환영입니다 :) 전체 포스트는 Algorithm 포스트에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
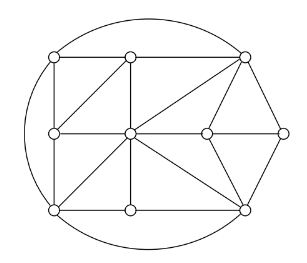
이번에 살펴볼 <Independent Set>, <Vertex Cover>, 그리고 <Clique> 모두 그래프 위에서 정의되는 Search Problem이다. 그리고 3가지 문제 모두 서로 동치다!
Independent Set Problem
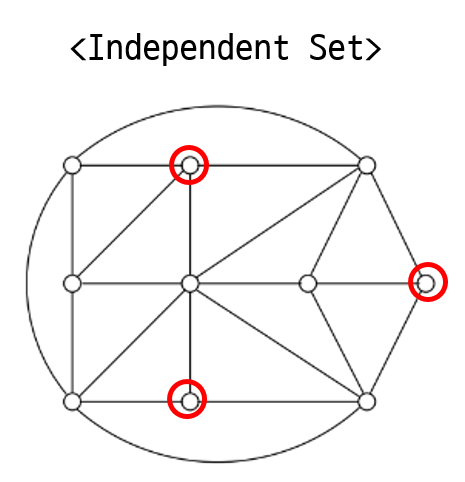
Problem. Independent Set Problem
Given a graph and a goal $g$, find $g$ vertices that are independent, that is, no two of which have an edge btw them.
이 문제는 예전에 DP 챕터에서 트리(Tree) 버전에서 살펴본 적이 있다: Independent Sets in Tree 이 경우는 DP 테크닉을 통해 선형 시간 만에 답을 구할 수 있다. 그러나 이번에는 그래프(Graph) 위에서의 Independent Set Problem이다. 그래프 위에서는 polynomial time algorithm이 존재하지 않는다.
Vertex Cover Problem
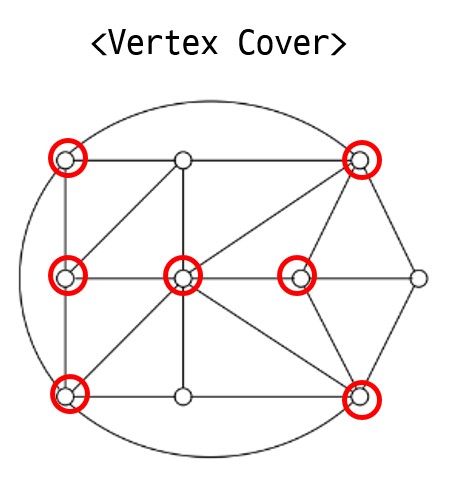
Problem. Vertex Cover Problem
Given a graph and a budget $b$, find $b$ vertices that cover every edge.
<Vertex Cover> 문제의 경우, <Set Cover> 문제의 특수한 경우라고 한다. 그전에 <Set Cover> 문제란 뭘까?
Problem. Set Cover Problem
Given a set $B$ and its subsets $S_1, …, S_m \subseteq B$, find a selection of the $S_i$ whose union is $B$. The number of sets picked should be minimized.
<Vertex Cover> 문제는 커버해야 할 집합을 edge set $E$로 두고, 각 노드 $v_i$에 연결된 edge subset을 $S_i$로 제시된 <Set Cover> 문제의 일종이다. <Set Cover> 문제의 경우, polynomial time algorithm은 존재하지 않고, Greedy Algorithm을 통한 근사(approximation) 알고리즘이 존재한다. 추후에 별도의 포스트를 통해 <Set Cover> 문제에 대해 더 살펴보겠다.
Clique Problem
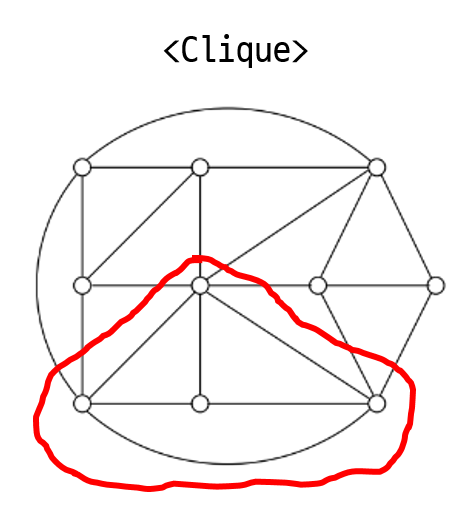
<Clique>는 “complete subgraph”로 부분 그래프 중 complete graph인 녀석을 말한다. 그래서 그래프 위에서 정의된 <Clique Problem>은 다음과 같다.
Problem. Clique Problem
Given a graph with $n$ vertices and a budget $b$, find a set of $b$ vertices such that all possible edges tw tem are present.
Reduction
Independent Set and Vertex Cover
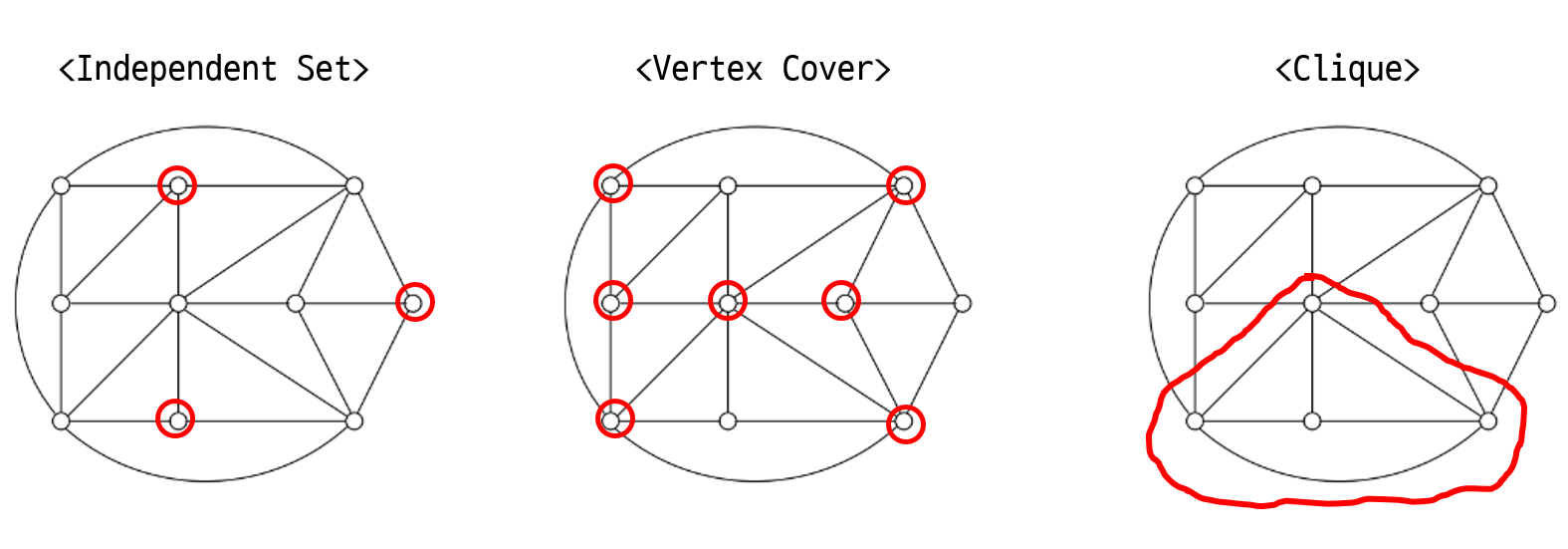
<Independent Set> 문제와 <Vertex Cover> 문제는 서로 동치이다! 위의 결과를 보면 알 수 있듯, <Independent Set> 문제에서 선택된 정점을 제외한 정점들이 <Vertex Cover> 문제의 solution임을 확인할 수 있다.
Claim.
$\equiv_P$는 “polynomial-time equivalent”라는 의미이다. 이것에 대해선 환원(reduction) 파트에서 자세히 살펴보겠다.
Proof.
We will show $S$ is an independent set iff $V \setminus S$ is a vertex cover.
($\implies$)
Let $S$ be any independent set. Consider an arbitrary edge $(u, v)$. Since $S$ is an independent set, any edge $(u, v)$ in $G$ don’t have the ends on $S$. This means it cannot be $u \in S$ and $v \in S$, so $u \notin S$ or $v \notin S$. This implies that $u \in V \setminus S$ or $v \in V \setminus S$. It is enough to cover an edge $(u, v)$ that one of end belongs to $V \setminus S$. Thus, $V \setminus S$ covers $(u, v)$.
($\impliedby$)
Let $V \setminus S$ be any vertex cover. Consider two nodes $u \in S$ and $v \in S$. This means two vertices $u$, $v$ is not in $V \setminus S$. Since $V \setminus S$ is a vertex cover, this non-existence means the graph does not have edge $(u, v)$. (If two nodes have an edge, one of two should be in a vertex cover $V \setminus S$) Thus, no two nodes in $S$ are joined by an edge, which implies that $S$ is an independent set.
Independent Set and Clique
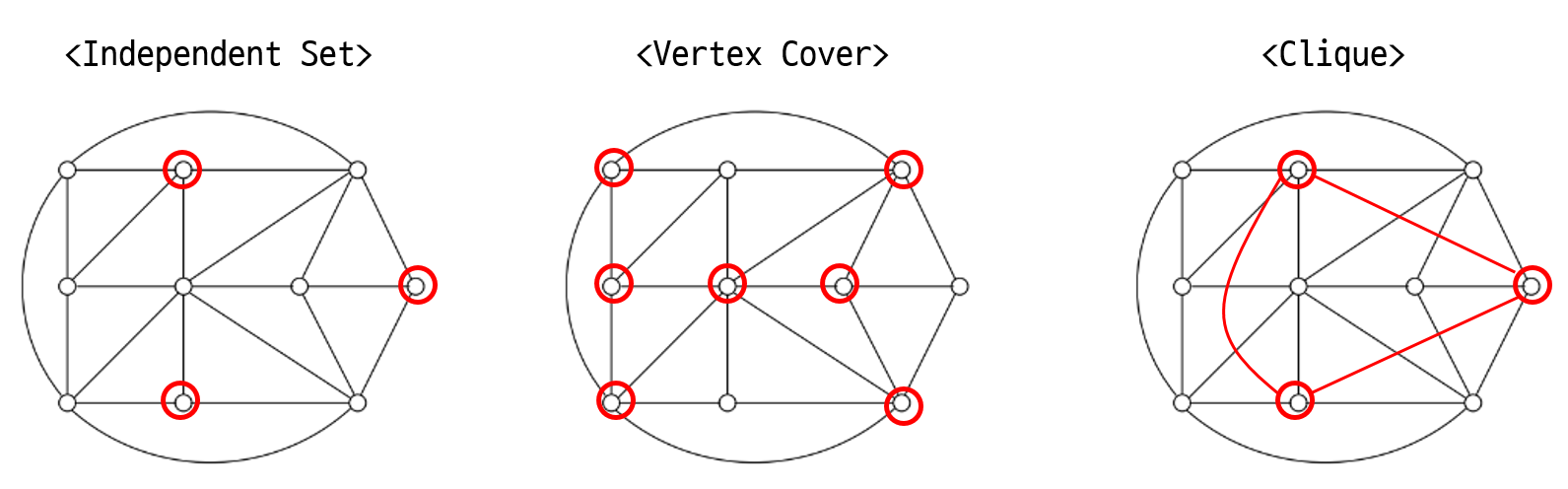
이번에는 <Independent Set> 문제와 <Clique> 문제를 살펴보자. 두 문제 역시 동치인데, 방법은 아래와 같다.
For a graph $G = (V, E)$, define the complement graph $\bar{G} = (V, \bar{E})$. Then, an independent set $S$ of $G$ is a clique of $\bar{G}$.
즉, <Clique> 문제를 풀고 싶다면, 주어진 그래프의 complement를 취해 <Independent Set> 문제를 풀면 되는 것이다!
